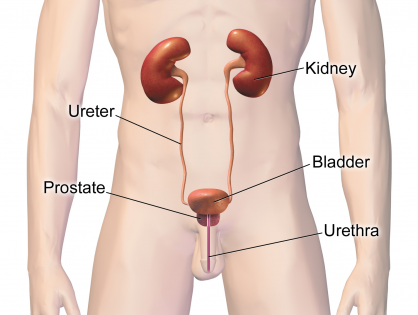
Urinary tract infections (more commonly referred to as UTIs) occur when germs or bacteria enter the opening of the urethra and then starts to multiply within any part of the urinary system - the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. It is most common to develop a UTI in the lower portion of the urinary tract, which includes your bladder and urethra, than it is in the upper urinary tract - the kidneys and ureters. UTIs are among the most commonly seen infections in humans, typically developing more frequently in woman; however, it is possible for men to get urinary tract infections. Although rare in males under 50 years of age, they can re-occur more frequently in men after the first UTI occurrence is treated.
What are the Symptoms of a UTI?
The symptoms of a urinary tract infection differ, being dependent on what part of the urinary tract is infected.
Lower Tract UTI (bladder and urethra) Symptoms
- Increased frequency of urination, including waking from sleep to urinate
- Painful or burning urination
- Increased urgency to urinate without passing much urine
- Cloudy urine
- Bloody urine
- Dark urine that looks like cola or tea
- Foul/strong smelling urine
- Leaking urine
- Pelvic pain in women
- Rectal pain in men
The most commonly seen symptom that most men experience with a UTI is dysuria, or painful urination. Initial onset symptoms of slow stream, hesitancy and urine dribbling account for only about one-third (33%) of the predictive UTI symptoms. Dysuria, urinary urgency and frequent urination with very little output occur for approximately three-quarters (75%) of the predictive and noticeable symptoms in males with UTIs.
Upper Tract UTI Symptoms (kidneys and ureters)
- Fever
- Chills
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Upper back and side pain and tenderness
Since upper tract UTIs affect the kidneys, they have the potential to become life threatening if the bacteria in the infected kidney moves into the blood. This can actually result in a condition called urosepsis, causing dangerously low blood pressure, shock and death.
Increased Risk of Getting a UTI
There are many factors that can increase your risk of developing a urinary tract infection. Anything that causes irritation in the urinary tract or any decrease in bladder output can lead to a UTI. The most common factors include:
Age — older adults are more likely to get UTIs
A previous UTI — you are more likely to develop another UTI after having had one previously
Urinary tract problems – obstructions or blockages, such as an enlarged prostate, plus certain forms of cancer or kidney stones
Prostate problems – a symptom in only men, an infected prostate or enlarged prostate gland may significantly increase the chances for a UTI
Prolonged use of urinary catheters – can make it easier for bacteria to enter your urinary system
Weak immune systems – systems that have trouble fighting infections are unable to fight off the bacteria that causes the UTI
Not being circumcised – germs can become trapped in the foreskin of the penis and enter into a man's urinary tract
Sexual intercourse – having a partner with a urinary tract infection increases the chances of developing a UTI
The Diagnosis and Treatment of UTIs
Testing for a urinary tract infection requires a sample of your urine in order to learn what type of bacteria maybe be responsible for causing the infection. This sample is usually collected from what's known as a "mid-urine stream", rather than at the beginning, in order to avoid contamination from the bacteria or yeast that may be on your skin. The urine test will also look for high numbers of white blood cells, which may indicate that an infection is causing the symptoms that the patient is experiencing. A urine culture may also be performed to test for bacteria or fungi, identifying the cause of the infection and assisting in the selection of the correct treatment for the infection. If after treatment, your UTI does not get better, or you have a re-occurrence, you may have to have imaging tests done to look for an infection in your kidneys, any urinary tract damage, blockages, or any other problems.
The course of treatment selected depends on the cause of the UTI, determined by the test results from diagnosis. In most scenarios, bacteria is the cause and the UTI will be treated with antibiotics. If the UTI is caused by a virus, it will be treated with an antiviral medication, such as cidofovir. Fungal urinary tract infections are treated with an antifungal medication, such as fluconazole.
Questions about UTIs? Contact Philadelphia Urology Associates for Answers
If you or a loved one are experiencing a urinary tract infection (UTI), please contact Philadelphia Urology Associates online for an appointment today or call us now at 215-563-1199. Dr Sloane and his team are experts in the field and can offer you the help you deserve.
At Philadelphia Urology Associates, Dr. Bruce Sloane is a nationally renowned specialist in Men's Health issues and Age Management Medicine. Throughout Philadelphia and the surrounding areas, patients seek his expertise to treat premature ejaculation and other sexual performance issues. Using state-of-the-art equipment and having extensive specialized education and training, Dr. Sloane will find the treatments and solutions that will work for you.